Dominion of Vancouver Island
This article or section is in the middle of an expansion or major restructuring. You are welcome to assist in its construction by editing it as well. If this article has not been edited in several days, please remove this template. |
Island of Vancouver and its Dependencies Isla de Vancouver y sus Dependencias (Spanish) | |
|---|---|
| Motto: Occidente ultra Occidentem (Latin) "The West beyond the West" | |
| Anthem: "God Save the King" | |
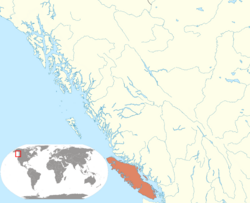 Territory claimed by the Dominion of Vancouver Island (orange) in North America (beige). | |
| Status | Active |
| Capital | Cookstown |
| Official languages | English, Spanish |
| Recognised regional languages | Pacific Northwest languages |
| Ethnic groups (2024) |
|
| Religion (2024) |
|
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
• Monarch | Charles III[a] |
| Dustin Carlson | |
• Prime Minister | Lucas Gonyer |
| Legislature | Legislative Assembly |
| Independence from Canada | |
• Established | 15 July 2019 |
• Act of Union with British San Juan Islands | 1 June 2023 |
| Area | |
• Total | 32,305.94 km2 (12,473.39 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2023 census | 13 |
| HDI | 0.944 very high |
| Currency | Vancouver Island Pound (£) (VIP) |
| Time zone | UTC−8 (PST) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC−7 (PDT) |
| Date format | mm/dd/yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +1 |
| Internet TLD | .ca |
Website example | |
The Dominion of Vancouver Island, officially the Island of Vancouver and its Dependencies (Spanish: Isla de Vancouver y sus Dependencias), is a North American micronation located on Vancouver Island in the Canadian province of British Columbia. Founded by Dustin Carlson in 2019, its government claims to be a restoration of the 19th century British colony that comprised Vancouver Island and the Gulf Islands of the Georgia. The dominion has declared its independence from Canada but its existence is not formally recognized by the United Nations or the government of any sovereign state.[1]
It is governed by a parliamentary constitutional monarchy that recognizes Charles III as its king and head of state, although this claim has not been acknowledged by the King. The Governor-General of Vancouver Island acts as the de facto head of state in day-to-day affairs while an elected prime minister serves as head of government. The Legislative Assembly is the country's unicameral legislature responsible for governance and passing legislation. The Dominion of Vancouver Island seeks to receive status as a Commonwealth realm and international recognition, despite many of its aspects and territorial claims being lighthearted and theatrical in nature. It has a moderate political ideology and a strong tradition of social and economic liberalism.
The foreign policy of the dominion is focused on diplomacy with other micronations and independence movements, as well as pressing its rights to self-determination across the wider international community. It has a current population of 23 citizens living on Vancouver Island as well as abroad, and regularly issues its own passports and currency.
Etymology
Indigenous peoples have inhabited Vancouver Island for thousands of years, long before the arrival of Spanish and British naval expeditions in the late 18th century, and had numerous local names for the island and its immediate surroundings. The Spanish and British originally agreed to name it Quadra's and Vancouver's Island in commemoration of the 1792 negotiations between Spanish commander Juan Francisco de la Bodega y Quadra and British naval captain George Vancouver, to resolve the Nootka Crisis. Over the following decades, Bodega y Quadra's name was eventually dropped as the British increased exploration and settlement of the area. In 1849, the Colony of Vancouver Island was established, officially known as the Island of Vancouver and its Dependencies.
Upon the former colony's modern revival as a micronation in 2019, Island of Vancouver and its Dependencies was once again adopted as the official name. Dominion of Vancouver Island was selected as a shorter name for common use, with the prefix dominion chosen to differentiate it from its colonial predecessor. Citizens of the country use the demonym "Vanisler" or the more common "Vancouver Islander."
History
The history of the Dominion of Vancouver Island dates back to early 2019. Canadian citizen Dustin Carlson developed an interest in micronations after watching a YouTube video about the Republic of Molossia, and began researching the history of self-proclaimed states in greater detail. Initially adopting a socialist model of government, Carlson began laying the groundwork for a functioning nation state. Finding this style of governance too problematic to establish a working economy for the fledgling country, Carlson soon abandoned socialism and instead decided to adopt a constitutional monarchy with a Westminster system of parliamentary democracy.
Carlson held a long-time interest in the history of Vancouver Island and the subsequent colony that was established by the Hudson's Bay Company in 1849. A decision was made by Carlson, and a small number of family and friends who had joined the project, to reestablish the former colony as a modern sovereign state. On 15 July 2019, the Dominion of Vancouver Island declared its independence from Canada, with Carlson becoming its inaugural governor-general. The newly established country adopted the flag of Vancouver Island, designed by Michael Halleran in 1988, as its official national flag, and was assisted by fellow micronationalist Ronnie Miller who created an updated version of the former colony's Great Seal. Carlson chose Occidente ultra Occidentem (The West beyond the West) as the dominion's national motto. The inspiration for the motto comes from historian Jean Barman, who published the book "The West Beyond The West" about British Columbian history in 1991.[2]
Since its foundation in 2019, the micronation has experienced several periods of inactivity, culminating in a complete cessation of government functions in early 2023. Activity resumed in December of that year as the Dominion of Vancouver Island elected Lucas Gonyer as its new prime minister, who quickly set about restructuring ministerial positions and saw to the appointment of several new officials in key posts.
Politics and government
The Dominion of Vancouver Island has a responsible government based upon a parliamentary system within the context of a constitutional monarchy.
Monarch
Charles III is recognized as the King of Vancouver Island, although this position has not been acknowledged by His Majesty. As an unrecognized micronation, the powers of the Vancouver Island monarch are mostly ceremonial although the King is legally considered the nation's de jure head of state due to his title as the King of Canada, and Vancouver Island existing entirely within his sovereign realm. Her Late Majesty Queen Elizabeth II was the first monarch of the dominion, until her passing in 2022.
Governor-General
The Governor-General of Vancouver Island is the nation's de facto head of state acting "in His Majesty's name and on His Majesty's behalf" in the absence of the monarch. Unlike the 15 Commonwealth realms where the governor-general is directly appointed by the King on the advice of the prime minister, Vancouver Island governor-generals are appointed by the legislature due the country's political status as a micronation. The position has no fixed term limit, with the governor-general serving at At His Majesty's pleasure so long as he/she enjoys the confidence of the legislature. Dustin Carlson has been the country's first and only governor-general since its establishment in 2019.
Prime Minister
The dominion's head of government is the Prime Minister of Vancouver Island, a civil service position directly elected by its citizens. The prime minister serves a term of four years, which can be extended an additional two years at the request of the legislative body or a public referendum. Lucas Gonyer is the current prime minister, after winning the dominion's most recent election on 7 December 2023.
Legislative Assembly
The country's unicameral legislature is the Legislative Assembly, which consists of 6 elected members. Sittings of the Legislative Assembly are normally held at Government House, the de facto headquarters and personal residence of the governor-general. The constitution stipulates that there must be at least one meeting of the Legislative Assembly every six months, although the Assembly can meet more frequently at the discretion of the prime minister.
Law and order
Article VI of the dominion's constitution states that all Vanislers shall have the same legal rights that they enjoy in Canada. Article VI Section II requireds every citizen to obey all Canadian federal and provincial laws at all times. The same rule applies to its citizens living abroad with regards to the laws of their home countries. The Supreme Court of Vancouver Island handles all internal disputes within the micronation, while the Vancouver Island Dominion Police (VIDP) Is the territorial police force responsible for law enforcement.
Ministries
Their are nine active ministries in the dominion:
- Ministry of the Viceregal Household
- Ministry of State
- Ministry of Foreign Relations
- Ministry of War
- Ministry of the Interior
- Ministry of the Treasury
- Ministry of Justice
- Ministry of the Environment
- Ministry of Development
Foreign relations
Since its foundation in 2019, the dominion has appointed several diplomatic agents abroad to press its rights for self-determination. While not formally recognized by the government of any macronation or intergovernmental organization, its government unilaterally recognizes the sovereignty of over 200 nations, both in the maconational and micronational spheres. It is a founding member of CATO as well as a member of the United Sovereignties and the Union Against Micronational War. The dominion is also a signatory of the Wrythe Convention, and Montediszamble Convention.
Unilateral recognition
 All United Nations member states
All United Nations member states British West Florida
British West Florida Bumbunga
Bumbunga Cook Islands
Cook Islands Flandrensis
Flandrensis Haida Nation
Haida Nation Holy See
Holy See Lostisland
Lostisland Manchukuo
Manchukuo Molossia
Molossia Niue
Niue Palestine
Palestine Sancratosia
Sancratosia Sealand
Sealand Slowjamastan
Slowjamastan Somaliland
Somaliland Taiwan
Taiwan Westarctica
Westarctica
Mutual recognition
| Name | Date |
|---|---|
| 19 July 2020 | |
| 20 November 2020 | |
| 10 January 2021 | |
| 15 January 2021 | |
| 22 January 2021 | |
| 29 January 2021 | |
| 21 February 2021 | |
| 26 February 2021 | |
| 4 March 2021 | |
| 16 March 2021 | |
| 30 March 2021 | |
| 21 April 2021 | |
| 5 May 2021 | |
| 1 June 2021 | |
| 1 June 2021 | |
| 27 September 2021 | |
| 21 March 2022 | |
| 23 April 2022 | |
| 27 May 2023 |
Recognition refused
Geography and climate
Although the dominion's government claims the entirety of Vancouver Island and the adjacent Gulf Islands as its sovereign territory, these claims are viewed as purely ceremonial by its citizens as well as outside observers due to the micronation lacking any legal or physical jurisdiction over the region. Its physical territorial possessions are limited to two small residential properties totaling 0.36 acres in combined size. The larger of the two, Cookstown, acts as the nation's de facto capital. Cookstown is situated entirely within Canadian sovereign territory, and is located on the eastern coast of central Vancouver Island near the Canadian town of Comox. Bordered by forests on two sides and residential housing on the remaining two, its local geography features a large flower garden, Koi pond, and numerous vegetable crops. Two large Douglas fir trees provide shade to the northern portion of the property, which houses a gazebo for hosting diplomatic summits. Government House, the personal residence of the governor-general and his family, is located along Cookstown's eastern boundary and includes street access via its main border crossing with Canada.
Cookstown has a Mediterranean climate according to the Köppen climate classification. Summers are hot and dry, with frequent heat and wildfire warnings, while winters are typically mild, but can experience heavy rain and snowfall at times.
| Climate data for Cookstown | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 6.4 (43.5) |
7.4 (45.3) |
9.6 (49.3) |
12.9 (55.2) |
16.6 (61.9) |
19.8 (67.6) |
22.8 (73) |
22.7 (72.9) |
19.0 (66.2) |
12.9 (55.2) |
8.5 (47.3) |
5.9 (42.6) |
13.7 (56.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 1.4 (34.5) |
1.2 (34.2) |
2.5 (36.5) |
4.6 (40.3) |
8.0 (46.4) |
11.1 (52) |
13.3 (55.9) |
13 (55) |
9.9 (49.8) |
6.0 (42.8) |
2.9 (37.2) |
0.9 (33.6) |
6.2 (43.2) |
| Source: Environment Canada[3] | |||||||||||||
Economy
The Dominion of Vancouver Island is ranked 0.944 on the Human Development Index and is considered a moderately developed micronation with a CGSC classification of 3.2. It has a small but highly diversified market economy that is almost entirely dependent on Canada for its essential goods and services. A heavy reliance on agriculture is utilized for the exportation of eggs and vegetables to Canada as well as localized trade within the micronation itself, with the Canadian dollar being widely accepted in all transactions.
The Vancouver Island Pound (VIP) is the nation's official currency and is printed and circulated by the Bank of Vancouver Island. The VIP is not backed by hard assets, but simply by a promise to pay the bearer upon the the prospect of recognition of the Vancouver Island as an independent state by the United Nations General Assembly.
Culture
Vanisler culture is deeply inspired by the environment and people of the surrounding Cascadia bioregion. Western alienation plays a significant role in Vanisler individualism, as well as the belief that Vancouver Island is a region that is distinctively unique from the rest of Canada.
The Dominion of Vancouver Island is a multicultural nation with an abundance of Anglo-Canadian and Indigenous cultural influences. The languages, history and traditions of Indigenous people are widely promoted and legally protected within the micronation, with a strong focus on environmentalism.
National symbols
-
National flag
-
Viceregal Standard
-
Royal Standard
-
Coat of arms
Holidays
| Date | Name | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| 1 January | New Year's Day | Celebrates the start of the new year. |
| Third Monday in February | Family Day | Shared statutory holiday with British Columbia. |
| Between 20 March and 23 April | Good Friday | Commemorates the crucifixion of Jesus, on the Friday before Easter. |
| 15 May | President Baugh Day | Honors Kevin Baugh, President of the Republic of Molossia and original inspiration for the establishment of a micronation. Dustin Carlson first watched a documentary about Molossia on this day in 2019. |
| Second Monday in June | King's Official Birthday | Celebrates the birth of the Sovereign, King Charles III. |
| 15 July | Sovereignty Day | Celebrates the foundation of the Dominion of Vancouver Island |
| 22 October | Founder's Day | Celebrates of the birth of Dustin Carlson, founding father and inaugural governor-general of Vancouver Island. |
| 11 November | Remembrance Day | Memorial holiday shared with Canada. Honors Canada's war dead. Anniversary of the armistice ending World War I in 1918. |
| 25 December | Christmas Day | Commemoration of the birth of Jesus of Nazareth. |
Gallery
-
Flag of Vancouver Island, flying outdoors in the dominion.
-
Interior of Government House, with national flag on display.
-
National animal and government mascot of the dominion, the beaver.
See also
Notes
- ↑ Charles III does not recognize the Dominion of the Vancouver Island, and has not claimed the throne officially.
- ↑ The Dominion of Vancouver Island currently recognizes the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan as the government of Afghanistan instead of the de facto ruling government, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan.
References
- ↑ "Independent States of the World" nationsonline.org
- ↑ "The West Beyond the West" utorontopress.com
- ↑ Environment Canada—Canadian Climate Normals 1971–2000, accessed July 5, 2012








