Administrative divisions of Græcia
| Administrative divisions of Græcia | |
|---|---|
| Also known as: Διοικητικὴ διαίρεσις τῆς Γραικίας (Hellenic) SVBDĪVĪSIŌ GRÆCIÆ (N. Latin) Вꙑправитєльнъ орздѣлъ Грѣкійꙑ (S. Ruthenian) 𐌊𐌄𐌓𐌇 𐌇𐌄𐌌 𐌞𐌉𐌀𐌍𐌝𐌕𐌓𐌀 (Græcian) | |
 | |
| Category | Unitary microstate |
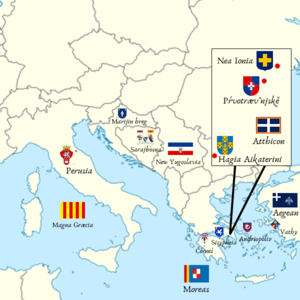
| Location | |
| Created | 14 October 2020 AD 25 February 2021 AD 10 June 2022 AD (current) |
| Number | 20: 5 voivodeships, 11 boroughs, 6 districts (as of 2024) |
| Possible types | Voivodeship Borough District |
| Populations | TBD |
| Areas | TBD |
| Government | Voivode High Burghermaster (or mistress) District council |
| Subdivisions | Borough District n/a |
Following the re-organisation on 25 February 2021 AD, the administrative divisions of Græcia consist of three main levels: the voivodeships, the boroughs, and the districts. The previous top-level administrative division were the boroughs of Græcia, but the need for collective representation lead the Senate to decide the reform. Although one of the voivodeships accounts for a single borough, it is not considered an autonomous self-governing entity.
Administrative divisions
Voivodeships
The top level is composed of the voivodeships (Hellenic: Βοεβοδάτα, Voevoðáta; sing. Βοεβοδάτον, Voevoðáton; Neoclassical Latin: PALĀTĪNĀTĪ, sing. PALĀTĪNĀTVS; South Ruthenian: Воѥводьства, Vojevod'stva; sing. Воѥводьство, Vojevod'stvo; Græcian: 𐌇𐌄𐌌 𐌞𐌉𐌄𐌍𐌈𐌝𐌓𐌐𐌄𐌞𐌋𐌋𐌄𐌁, BELLUEPRⱵÐNEIU MEH; sing. 𐌇𐌄𐌌 𐌞𐌄𐌍𐌈𐌝𐌓𐌐𐌄𐌞𐌋𐌋𐌄𐌁, BELLUEPRⱵÐNEU MEH), governed by a voivode (Hellenic: Βοεβόδας, Voevóðas; Neoclassical Latin: VOIVODA; South Ruthenian: Воѥвода, Vojevoda; Græcian: 𐌄𐌍𐌈𐌝𐌓𐌐𐌄𐌞𐌋𐌋𐌄𐌁, BELLUPRⱵÐNE). The Voivode is always appointed by the Governor.
Boroughs
- See: Boroughs of Græcia
The second level is composed of the boroughs (Hellenic: Ϝάστη, Wástī; sing. Ϝάστυ, Wásty; Neoclassical Latin: BVRGĪ, sing. BVRGVS; South Ruthenian: Ґорді, Gordi; sing. Ґордъ, Gordě; Græcian: 𐌉𐌍𐌔𐌖𐌄𐌂, CEYSNI; sing. 𐌍𐌝𐌔𐌖𐌄𐌂, CEYSⱵN), governed by a high burghermaster (or mistress) (Hellenic: Ὑψηλὸς Μάγιστρος, Hypsīlòs Májistros; Neoclassical Latin: MAGISTER ALTVS; South Ruthenian: Вꙑсокъ Маѓістръ, Vîsokě Maǵistrě; Græcian: 𐌇𐌀𐌌 𐌉𐌔𐌀𐌗𐌄𐌂, CEXASI MAH). The High Burghermaster (or mistress) is always appointed by the Governor.
Districts
- See: Districts of Græcia
The lowest level is composed of the districts (Hellenic: Δῆμοι, Ðī̃mi; sing. Δῆμος, Ðī̃mos; Neoclassical Latin: PĀGĪ, sing. PĀGVS; South Ruthenian: Объкрѫѕі, Oběkrǫdzi; sing. Объкрѫґъ, Oběkrǫgě, Græcian: 𐌉𐌌𐌖𐌋𐌈𐌄𐌌, MEÐLYMI; sing. 𐌌𐌖𐌋𐌈𐌄𐌌, MEÐLYM), run by the district council (Hellenic: Ἐκκλησία τοῦ Δήμου, Ekklīsía tũ Ðī́mu; Neoclassical Latin: CŌNSILIVM PĀGĪ; South Ruthenian: Съвѣтъ объкрѫґа, Sěvætě oběkrǫga; Græcian: 𐌌𐌖𐌋𐌈𐌄𐌌 𐌅𐌀𐌕𐌖𐌈 𐌇𐌄𐌌, MEH ÐYTAǷ MEÐLYM), popularly elected every 5 years.
Special Administrative Divisions
Free City
An unranked level, the Free City (Hellenic: Ἐλευθέρα Πόλις, Elefþéra Pólis; Neoclassical Latin: VRBS LĪBERA; South Ruthenian: Вольнъ Ґордъ, Voljně Gordě; Græcian: 𐌍𐌝𐌈𐌖𐌀𐌋 Ↄ𐌍𐌔𐌖𐌄𐌂, CEYSNĚ LAYÐⱵN), run by the Consul (Hellenic: Ὕπατος, Hýpatos; Neoclassical Latin: CŌNSVL; South Ruthenian: Кѡнсоулъ, Kōnsoulĕ; Græcian: 𐌋𐌖𐌔𐌍𐌞𐌂, CUNSYL), is basically a city-state, operated as a semi-autonomous entity within Græcia. The Consul is always appointed by the government, with the final approval belonging to the Governor himself.
Protectorates
An unranked level, the protectorates (Hellenic: Προτεκτοράτα, Protektoráta; sing. Προτεκτοράτον, Protektoráton; Neoclassical Latin: PRŌTECTORĀTA; sing. PRŌTECTORĀTVM; South Ruthenian: Протєктораті, Protektorati; sing. Протєкторатъ, Protektoratě; Græcian: 𐌞𐌖𐌑𐌖𐌂 𐌉𐌇𐌄𐌌, MEHI CYŚYU; sing. 𐌞𐌖𐌑𐌖𐌂 𐌇𐌄𐌌, MEH CYŚYU) are entities that are protected by the Græcian state. The governor of Græcia serves as the protector. Each protectorate operates under different, agreed upon sets of rules, essentially under a similar framework.