Republic of Leppä
This article contains too many red links, and may be going through a major copy edit. You can help by clicking on red links and creating articles or by removing unnecessary red links. |
Republic of Leppä [Republiek Leppä] Error: {{Lang}}: unrecognized language code: du (help) Leppä Tasavalta Leppä Респу́блика | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Small Country, Big Aspirations" (English) | |
Government Wordmark | |
  | |
| Capital and largest city | |
| Official languages | Dutch English Finnish Russian |
| Ethnic groups | Leppän 97% Others 3% |
| Demonym(s) | Leppän |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary republic with an executive Presidency |
| Shady Morsi | |
• Deputy Chief-Executive | Alan Amin |
• Chief Justice | Anne Voogd |
| Legislature | Chamber of Deputies |
| Landsdag | |
| Population | |
• Census | 66 |
| Currency | Leppan Pound (PND) |
| Time zone | UTC (WET) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+1 (WEST) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy yyyy-mm-dd (AD) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +31 (Kennedien) +358 (Leppäluto) |
| Internet TLD | .lp |
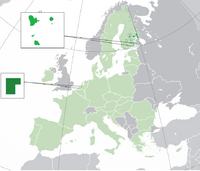
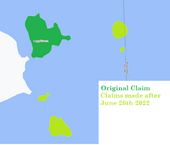
Leppä offically known as Republic of Leppä also spelled as Leppa is a self proclaimed independent archipelagic state , commonly refered as a micronation. Leppä consists of 4 main claims. The islands of Leppäluto, Toivonsaari and Kivsiä located in the Virolahti bay and borders Russia to the east and Finland to the west, north and south and Kennedien which is surrounded by the Netherlands, With an area of approximately 700 metres (660 ft) long and 110 metres (360 ft) wide. it is the smallest state in the world by both area and population. Leppa is inspired by small city state's like San Marino, Singapore, Vatican City and Monaco, Leppa is a secessionist nation. Altough its secessionism is based on cultural rather than political goals Leppa is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on Kennedien, Leppa claims to be the spiritual sucessor of Wallenia and Medopolania, retaining its territory and citizenry, Altough Leppa has elected to declare Wallenia as Leppa's predecessor on 11 July 2022
The state is governed under a form of a republic, the Chief-Executive wields immense political power but is also part of parliament the Chief-Executive is the combined head of state and head of government legislative authority is vested in an elected, Chamber of Deputies and the Landsdag which is a meeting between the Chief Executive and the Governors of the regions
A nation that developed rapidly, Leppä ranks highly in international comparisons of national performance, such as quality of life, education, protection of civil liberties, government transparency, and economic freedom. Leppä as a nation state underwent major changes during the 2020s, which transformed it from various incarnations to an active member of the Microwiki community aswell a nation with its own idenity Nationally,
Leppä is not a member of the United Nations (UN), However many other states maintain unofficial ties through representative offices and institutions that function as de facto embassies and consulates. Leppa is a member of the Union Against Micronational War
Etymology
The name Leppä comes from the Finnish name of the island. Leppäluoto. luoto is an used Finnish suffix such as Koiluoto, the full name of the state is Republic of Leppä, Leppä can be pronounced as Lep-ä or Lep-pah
History
Pre-independence

Many ancient sites were discovered on the shores of the gulf dated to up to nine thousand years old. Humans began to inhabit these places soon after the ice age glaciers have retreated and the water level of the Littorina Sea lowered to reveal the land. Remains of about 11 Neolithic settlements were found since 1905 in the mouth of the river Sestra River (Leningrad Oblast). They contain arrow tips and scrapers made of quartz, numerous food utensils and traces of fire camps – all indicative of hunting rather than agricultural or animal husbandry activities.
The gulf coast was later populated by Finnic peoples. Eesti (or Chud) inhabited the region of the modern Estonia, Votes were living on the south of the gulf and Izhorians to the south of Neva River. Korela tribes settled to the west of Lake Ladoga. In the 8th and 9th centuries, the banks of Neva and of the Gulf of Finland was populated by East Slavs, in particular by Ilmen Slavs and Krivichs. They were engaged in slash-and-burn agriculture, animal husbandry, hunting and fishing. From the 8th to the 13th century, the Gulf of Finland and Neva were parts of the waterway from Scandinavia, through Eastern Europe to the Byzantine Empire.
From the 9th century, the eastern coast of the gulf belonged to Veliky Novgorod and were called Vodskaya Pyatina. As a result of the 1219 crusade and the Battle of Lindanise, the Northern Estonia became part of Denmark (Danish Estonia). In the 12th century, the city Reval (Latin: Revalia, Russian: Колыва́нь) was established on the territory of modern Tallinn. As a result of the Estonian uprising in 1343, the Northern Estonia was taken over by the Teutonic Order and sold by Denmark in 1346. In 1559, during the Livonian War, the Bishop of Ösel-Wiek in Old Livonia sold his lands to King Frederick II of Denmark for 30,000 thalers. The Danish king gave the territory to his younger brother Magnus who landed on Saaremaa with an army in 1560. The whole of Saaremaa became a Danish possession in 1573, and remained so until it was transferred to Sweden in 1645.
Russia reclaimed the eastern part of the gulf as a result of the victory in the Great Northern War (1700–1721). On 16 May 1703, Saint Petersburg was founded in the mouth of Neva River, not far from Nyen, and in 1712 it became Russia's capital. To protect the city from the Swedish fleet, the Kronshlot fortress was built on an artificial island near the Kotlin Island in May 1704. By 1705, five more such forts were built nearby composing the city Kronstadt. These fortifications, nicknamed by the contemporaries "the Russian Dardanelles", were designed to control the Gulf waterway.
Before World War I the Russian Emperor Nicholas II used to spend summers with his family in the archipelago of Virolahti with his yacht Standart, Finland being an autonomous province within the Russian Empire between 1809 and 1917.
Virolahti lost some of its area (over 100 km2 (39 sq mi)) to Soviet Union in Paris Peace Treaties, 1947, after World War II.
Wallenia
Independence


After long and various unsucessfull projects. Shady Morsi united with former citizens of his past micronations to form a pernament micronation Unlike with Shady Morsi’s other micronational projects. Morsi wanted to have a nation that fully commits to the 1933 Montevideo convention. And Leppa partialy did , Claims proposed was the internationaly divided Koiluoto, and nearby Kuusiluoto before settling for Leppäluoto, Leppa as a state of international law possessd the following qualifications: a defined territory; government; and capacity to enter into relations with the other states. Leppa however lacked a permanent population on Leppäluoto. Leppä argued that the Leppägovernment has 100 percent control on Kennedien and that Morsi even erected some borderstones and also a nation that was rather a pysical micronation with actual memorabilia “in the spirit of Molossia, Sealand and Shadyvinkenstein.” With the goal of establishing ‘’a new nation cultural-idealist project’’ Leppä was more secessionist oriented with the plan of actually sending an independence decleration of Leppä towards the King of the Netherlands and the President of Finland, However the latter has been delayed due to Finnish-Russian tensions
After winning the election due to a divided opposition , Shady Morsi was sworn in office on May 19, 2022 as the first chief executive, On June 26 the Republic of Leppä claimed 2 more islands aftrer a proposition from both the Chief-Executive and the Chamber of Deputies some, at first, largely cosmetic constitutional changes. where made to the flag in order to represent the recently claimed island this was partialy the result that the utility in the nation had changed. A large group of young people from Shady's college (which found Shady Morsi's microwiki page) applied to be citizens of the Republic of Leppa . This group ensured that the nation became much more active and larger,
Government
The Constitution of Leppa is the rule of law, which protects the citizens of Leppa and represents their rights. The politics of Leppa take place in a framework of a multi-party representative democratic republic, whereby the Chief-Executieve of Leppa is both head of state and head of government, and is elected by and accountable to the Chamber of Deputies of Leppa. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the Chamber of Deputies.
Executive
Chief-Executive
Deputy Chief-Executive

The Chief-Executive of Leppa is the head of state of Leppa The Chief-Executive is elected president by members of the Chambers of Deputies. These members state on the ballot who they would support for Chief-Executive if elected, and after election to the National Assembly vote for whomever they indicated they would elect as Chief-Executive. The Chief-Executive has the following requirements: (a) is a citizen of Leppa ; (b) has attained the age of 18 years; and (c) is qualified to be elected as a Member of the Chamber of Deputies. '
The executive power of Leppa resides solely in the Chief-Executive. The Chief-Executive is also the commander of the armed forces. The Chief-Executive also has the power to pardon a person convicted of a crime
The Deputy Chief Executive is chosen by the Chambers of Deputies. Its not uncommon that the Deputy Chief Executive is from the opposition party TheDeputy Chief Executive takes over for the Chief Executive when the Chief Executive is unable to fulfill his duties either because of illness, death, or other reasons.
Legislative

The Chamber of Deputies consists of the Chief-Executive and Chamber of Deputies. The Chief-Executive is a voting member of the Chamber of Deputies In order for a person to be eligible to be a member of the Assembly they must: be a citizen of Leppa , be 16 years old, is registered to vote, and is able to speak and read in English.
In addition to a CoD, Leppa also has a Chamber of Councilors. The Ntlo ya Dikgosi acts as an advisory body to the Chamber of Deputies This body consists of 12-150 members. In order to be eligible to be a member one must be 18 years old altough citizenship isnt required. The member is appointed as the Chief-Executives will. . This body possesses no legislative power, including approval or veto power, rather they advise the Chief-Executive and the Chamber of Deputies on bills and measures. The COD's powers are defined by the Constitution and they include: defining economic, legal and political relations in Leppa, preservation and use of its heritage and entering into alliances. The CoD has the right to deploy the Leppan Armed Forces abroad, and it may restrict some constitutional rights and liberties in wartime or in cases of imminent war or following natural disasters. The CoD amends the borders of Leppa or the Constitution, enacts legislation, passes the state budget, declares war and decides on cessation of hostilities, adopts parliamentary resolutions and bylaws, adopts long-term national security and defence strategies, implements civil supervision of the armed forces and security services, calls referenda, performs elections and appointments conforming to the constitution and applicable legislation, supervises operations of the Government and other civil services responsible to the parliament,
Political Parties
Leppa has operated under a two-party system since its foundation the major parties have been the Decleration of Independents, and the Red-Greens, they have been seen as a "Generic left and Generic right" party, altough the DOI is seen as big tent other parties in Leppa must promote the participation of the people in the democratic life of the country, contribute in the representation of the nation and citizens, and be the access through which citizens can participate in public office, through whatever programs, principles and ideals they postulate. All political parties must be registered with the National Electoral Comitee
Political factions represented in the Chamber of Deputies
| Party | Logo | Party Leader | Ideology(s) | Election Symbol | Seats in the Chamber of Deputies | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
Big Tent National conservatism Economic liberalism |
DOI | 12 / 21
| ||||
| Red-Greens | Punaisetvihreät | 
|
Alan Amin | Social democracy Green politics Socialism |
REDGREN | 7 / 21
| |
| The Liberals | Liberal | 
|
Youri Mulder | Civil Libertarianism | THEL | 2 / 21
| |
Judicature

The judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature.
It consists of a typical British-style court system of local Magistrates Courts, a High Court and a Court of Appeal. The High Court is a superior court of record with unlimited original jurisdiction to hear and determine any criminal, civil or constitutional cases under any law. Appeals can be heard by the Court of Appeal. The Head of the High Court is the Chief Justice.
The Court of Appeal is the highest and final court in the country and deals with appeals from the High Court and the Industrial Court. The Head of the Court of Appeal is the Judge President. The Supreme Court of Leppa acts as the supreme legal source, in which the court possesses unlimited original jurisdiction to hear any cases. The court has a Chief Justice as well as a number of other judges, in which the number is determined by the CoD. The Chief Justice is appointed by the Chief-Executive, as well as all of the other Justices but these can be advised to the President by the Chamber of Deputies. In order to be qualified to be a judge on this court one must have either been a judge, been an attorney, been a law professor with a law degree, or been a Chief Magistrate. Appointments to this court are until the person reaches the age of 70. The only other reason a judge would leave the high court is if the Chamber of Deputies decides the person is no longer able to properly perform their duties.
The Judicial Service Commission is created to help advise the Chief-Executive on judicial nominations. It consists of the Chief Justice, the President of the JSC the Attorney-General, the Chairman of the Public Service Commission, a member of the Law Society nominated by the Law Society, and a person of integrity and experience who is not a legal practitioner appointed by the Chief-Executive.
Admainstrative Divisions
Leppä consists of 4 main claims. Leppäluto, Toivonsaari and Kivsiä are islands located in the Virolahti bay and borders Russia to the east and Finland to the west, north and south and Kennedien which is surrounded by the Netherlands, Leppa is divided into 4 administrative districts: that overlaps with those 2 claims All districts are divided into municipalities (gemeenten), of which there are 5 (2022) The muncipalties , have a permanent constitutional status and, in comparison with the situation in other countries, a high degree of independence. However the govenrment determines the powers and responsibilities of its municipalities. These may include providing local government services such as education, medical and social services, public transportation, and tax collection. The degree of centralization varies from one municipality
Municipalities are generally governed by an executive headed by a president or mayor. by a municipal parliament, depending on the size of the municipality, and on cantonal and municipal law. In some cantons, foreigners who have lived for a certain time in Leppa are also allowed to participate in municipal politics. As at the cantonal and federal level, citizens enjoy political rights, including direct democratic ones, in their municipality.
Municipalities are financed through direct taxes (such as income tax), with rates varying more or less within a framework set by the government
| Flag | Name | Code | Location | Official Language | Governor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Countries | |||||

|
Kennedien | JFK | 
|
Dutch | Jelmer Handgraaf (R-G) (As Mayor of Kennedy City) ex-officio Governor of Kennedien |
|
Leppäluoto | LEP | 
|
Finnish Russian |
Juan Betancourt (IND) |
|
Toivonsaari | TOI | 
|
Finnish Russian |
Rutger van de Swam (IND) |

|
Kivsiä | KIV | 
|
Finnish Russian |
Anuar Laddas (IND) |
Foreign relations


Leppa's foreign policy has long been created by its leaders with the intention of finding ways to resolve domestic issues, sharing national values with others, and fostering peace and cooperation. In accordance with this worldview, Leppa's foreign policy is aimed at maintaining friendly relations with all countries, Due to obvious geographical reasons, relations with Nordic Micronations are most important. Leppa supports the concept of Nordic regionalism,
Since June 2022 Leppa sends a non-voting delegate to the Nordic Council which is appointed by the Chamber of Deputies, Altough the task of non-voting delegate has been limited to watching the open meetings of the Nordic Council live and directly report to the Chamber of Deputies
International Organisations
Recognised; no relations
 All member states of the UN
All member states of the UN Kurdistan
Kurdistan Palestine
Palestine Republic of China
Republic of China Vatican City
Vatican City BjornSocialist Republic
BjornSocialist Republic Republic of Jamtland
Republic of Jamtland Republic of Ladonia
Republic of Ladonia Principality of Pigeon Island
Principality of Pigeon Island Republic of Yusienia
Republic of Yusienia
Diplomatic Relations
International Treaties
Geography
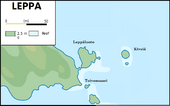
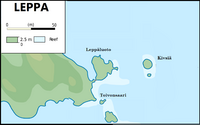
The Republic of Leppa consist of 4 areas. The islands of Leppäluto, Toivonsaari and Kivsiä located in the Virolahti Bay. The bay is about 10 km long. The Finnish part belongs to the municipality of Virolahti and the Russian part belongs to the municipality of Tienhaara in the Vyborg district . and Kennedien which is located in Oegstgeest
The nature of the state is fundamentally urban and none of the land is reserved for significant agriculture or other exploitation of natural resources. The territory holds many diverse structures that help provide autonomy for the sovereign state, including a bus stop, a port, radio station (with extraterritorial antennas in Netherlands), military barracks, government palaces and offices, public plaza, part of an audience hall, old defensive wall marking the border, institutions of higher learning, and cultural/art centers.
Kennedien

Kennedien is located in te Netherlands is the capital and most populous city of Leppa; with a population of 24 located within the Dutch mainland and surrounded by the Netherlands, It is also the seat of government of Leppa and hosts most of the Leppan companies and enterprises, Kennedy City the capital of the District of Kennedien,
Leppäluto, Toivonsaari and Kivsiä
Climate
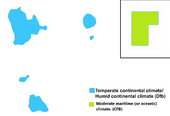
The predominant wind direction in Leppa is southwest, which causes a mild maritime climate, with moderately warm summers and cool winters, and typically high humidity. This is especially true close to the Leppan coastline,
In Köppen climate classification Leppa belongs to the Df group (continental subarctic or boreal climates). The southern coast is Dfb (humid continental mild summer, wet all year), and the rest of the country is Dfc (subarctic with cool summer, wet all year).The warm waters of the Gulf Stream and the North Atlantic Drift Current, play a big role in the climate of Norway, Sweden and Finland which continuously warm the region, if it weren't for these currents the winters in Scandinavia and Fennoscandia would be much colder. Westerly winds bring the warm air currents into the Baltic areas and to the country's shores, moderating winter temperatures, especially in the south and southwest in cities like Helsinki and Turku where winter highs tend to be between 0 and 5 °C (32 and 41 °F) but a cold snap like the one that occurred in mid-January 2016 can cause temperatures to plunge well below −20 °C (−4 °F). These winds, because of clouds associated with weather systems accompanying the westerlies, also decrease the amount of sunshine received during the summer. By contrast, the continental high pressure system situated over the Eurasian continent counteracts the maritime influences, occasionally causing severe winters and high temperatures in the summer.In Kennedien The predominant wind direction in is southwest, which causes a mild maritime climate, with moderately warm summers and cool winters, and typically high humidity.
| Climate data for Leppäluoto, Republic of Leppa | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 10.9 (51.6) |
11.8 (53.2) |
17.5 (63.5) |
25.5 (77.9) |
31.0 (87.8) |
33.8 (92.8) |
37.2 (99) |
33.8 (92.8) |
28.8 (83.8) |
21.1 (70) |
16.6 (61.9) |
11.3 (52.3) |
37.2 (99) |
| Record low °C (°F) | -51.5 (-60.7) |
-49.0 (-56.2) |
-44.3 (-47.7) |
-36.0 (-32.8) |
-24.6 (-12.3) |
-7.0 (19.4) |
-5.0 (23) |
-10.8 (12.6) |
-18.7 (-1.7) |
-31.8 (-25.2) |
-42.0 (-43.6) |
-47.0 (-52.6) |
−51.5 (−60.7) |
| Source: http://ilmatieteenlaitos.fi/lampotilaennatyksia | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Kennedien, Republic of Leppa | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 13.8 (56.8) |
15.9 (60.6) |
20.8 (69.4) |
25.9 (78.6) |
29.7 (85.5) |
33.5 (92.3) |
36.5 (97.7) |
34.6 (94.3) |
31.7 (89.1) |
24.5 (76.1) |
17.5 (63.5) |
15.4 (59.7) |
36.5 (97.7) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 5.9 (42.6) |
6.3 (43.3) |
9.3 (48.7) |
12.8 (55) |
16.7 (62.1) |
19.0 (66.2) |
21.3 (70.3) |
21.5 (70.7) |
18.4 (65.1) |
14.5 (58.1) |
9.9 (49.8) |
6.6 (43.9) |
13.5 (56.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 3.6 (38.5) |
3.6 (38.5) |
6.1 (43) |
8.7 (47.7) |
12.5 (54.5) |
15.1 (59.2) |
17.4 (63.3) |
17.5 (63.5) |
14.8 (58.6) |
11.3 (52.3) |
7.4 (45.3) |
4.3 (39.7) |
10.2 (50.4) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 1.0 (33.8) |
0.7 (33.3) |
2.7 (36.9) |
4.5 (40.1) |
8.1 (46.6) |
11.0 (51.8) |
13.3 (55.9) |
13.3 (55.9) |
10.9 (51.6) |
7.8 (46) |
4.5 (40.1) |
1.7 (35.1) |
6.6 (43.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | -16.4 (2.5) |
-14.0 (6.8) |
-11.1 (12) |
-4.4 (24.1) |
-1.5 (29.3) |
1.7 (35.1) |
5.4 (41.7) |
5.5 (41.9) |
1.2 (34.2) |
-4.4 (24.1) |
-7.1 (19.2) |
-10.6 (12.9) |
−16.4 (2.5) |
| Average Precipitation mm (inches) | 68.4 (2.693) |
51.2 (2.016) |
59.8 (2.354) |
42.9 (1.689) |
54.7 (2.154) |
61.6 (2.425) |
72.7 (2.862) |
84.0 (3.307) |
89.2 (3.512) |
89.9 (3.539) |
90.4 (3.559) |
76.4 (3.008) |
841.2 (33.118) |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 86 | 84 | 83 | 79 | 78 | 79 | 80 | 80 | 83 | 84 | 87 | 87 | 82.5 |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1 mm) | 12 | 10 | 11 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 13 | 132 |
| Average snowy days | 5 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 20 |
| Sunshine hours | 65.5 | 89.6 | 133.7 | 190.5 | 229.0 | 216.1 | 227.4 | 207.1 | 145.5 | 110.3 | 61.1 | 49.2 | 1,726.1 |
| Source no. 1: Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (1981–2010 normal, snowy days normal for 1971–2000)[1] | |||||||||||||
| Source no. 2: Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (1971–2000 extremes)[2] | |||||||||||||
Economy

Leppa has a mixed economy. Following a large scale privatisation process most of the companies in Leppa are now privately owned. Leppa has its own central bank, the Bank of Leppa , which issues its national currency, the Leppan pound. It is convertible at a freely floating exchange rate but only in Leppa .
The economy of Leppa is reliant on tourism and banking. Leppa has successfully sought to diversify into services and small, high-value-added, nonpolluting industries. Such as leasing the car collection of Jan Hendrick to car shows and crypto The state has no income tax The state retains monopolies in a number of sectors, including tobacco, the telephone network, and the postal service. Leppa has a prosperous and open economy, which depends heavily on foreign trade.
Military
The Leppan Defence Force has around 12 members dispersed between the line infantry regiment, service and support unit and coast guard. the LDF has the responsibility for several different roles: internal security, prevention of drug smuggling, the protection and support of fishing rights, prevention of marine pollution, search and rescue, ceremonial duties, assistance to government programs, provision of relief during natural disasters, assistance in the maintenance of essential services, and support of the police in maintaining law and order.
The LDF is one of the world's smallest militaries, consisting of 12 personnel. It is much better equipped for fulfilling its civil roles as opposed to providing a deterrence against would-be aggressors or in defending the nation during a war.
Culture


Leppa has been overshadowed by the culture of its neighbors. It retains a number of folk traditions, having been for much of its history a profoundly naval country. There are several notable museums, located mostly in Kennedy City. These include the Martin Museum, the National Museum and a small Museum for pluches. Although its contributions to the arts are not largely known outside its borders, Leppa has a rich cultural history, especially in classic cars, software development and photography.
The culture of Leppa is essentially a Western culture strongly influenced by Latin and Germanic culture and computer- and transit-related subcultures. The predominance of the English language, Protestant as the dominant religion and the high support for the Leppan Protestant Church
Another subculture that dominates Leppan society is 2010s futurism a subgenre of cyberpunk that reimagines late 00s early 10s popularized by its memes, technology and fashion. Notable elements of 2010s futurism includes rage comics, small pre android Samsung phones, DVD's and cars. Leppas predsucessor Medopolania's entry in the TVB Microvision Song Contest. the Riddle (a song released in 2009) is based on 2010s pop music
Media


Television and radio are provided by the Netherlands since Leppan programming is very irregular Like the Netherlands. Leppa shares the Dutch three television and five radio networks together with a number of commercial channels. All newspapers are privately owned.with the biggest being the Tijd Magazine, which is a direct clone of Time Magazine it published monthly, and consisting of articles about current events both in Leppa and abroad
Sport
Basketball, hockey and association football are most popular among men whereas swimming is most popular among women. Judo, volleyball and tennis are also very popular. The country's prime football league is the Staatsleague, which provides its national (association) football team with most players.
Holidays
Leppa has the lowest number of public holidays in the world. The Leppan description of a national holiday is either when its informaly celebrated or when its announced by the Leppan goverment, Leppa however does not maintain a mandatory paid holiday for everyone. It is custom for many employers to grant a paid holiday every 5 years on this day. Leppa however also observe Dutch and Finnish public hollidates
Health
Leppa has a universal multi-payer health care system paid for by a combination of statutory health insurance and private health insurance Leppa's health care system was 77% government-funded and 23% privately funded as of 2022
Demographics
Leppa had an estimated population of 81 inhabibants due to the claim of Kennedien overlapping with a flat building, though Leppa has about 71 registered citizens. It is the smallest populated country in Europe,
Life expectancy is high in Leppa though lesser than its neighbour 81.3 years for newborn girls and 80.7 The majority of the population of Leppa is ethnically Dutch. 40% Dutch, 10% Antillean and Aruban 10% Arab, 20% Others 10% Turkish, 5% Surinamese and Hindu, 5% Jewish, Leppas population is mostly concentrated in and around Kennedien, Altough some of the arent allfiliated with any region or district
Largest cities in Leppa
Ministry of Immigration | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | District | Pop. | |||||||
 Kennedy City  Chardonnay |
1 | Kennedy City | Kennedien | 12 |  Lynne | ||||
| 2 | Chardonnay | Kennedien | 9 | ||||||
| 3 | Lynne | Kennedien | 3 | ||||||
| 4 | Satamakaupunki | Leppäluoto | 3 | ||||||
| 5 | Mannerheim | Leppäluoto | 2 | ||||||
| 6 | Arras | Toivonsaari | 1 | ||||||
| 7 | [[{{{city_7}}}]] | [[{{{div_7}}}]] | {{{pop_7}}} | ||||||
| 8 | [[{{{city_8}}}]] | [[{{{div_8}}}]] | {{{pop_8}}} | ||||||
| 9 | [[{{{city_9}}}]] | [[{{{div_9}}}]] | {{{pop_9}}} | ||||||
| 10 | [[{{{city_10}}}]] | [[{{{div_10}}}]] | {{{pop_10}}} | ||||||
Gender

Leppa has a very huge gender inbalance. from the 71 citizens. Only 6% (6) identified as female. 93% identified as a male and 1% as non-binary/others Leppa has full gender equality for its citizens. Most of the Leppan Women are active in politics and has 3 female MP's Making Leppa the country with the highest female participation in politics The currently highest ranking woman in the Leppan government is Anne Voogt, Chief Justice. Third in line of the Chief-Executive, Women in Leppa are a monolithic group, all 6 of them are white cis Europeans
LGBT
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender (LGBT) rights in Leppa have been some of the most progressive in the world. this has mainly an impact from the macronation Leppa seceeded from, recent polls indicating that more than 78% of Leppa people support same-sex marriage. Organizations offering conversion therapy, the pseudoscientific practice of attempting to change an individual's sexual orientation or gender identity using psychological or spiritual interventions, are banned in Leppa by the Leppan constitution
Religion
Leppa's population is predominantly atheist with 50% saying "they dont belive in god" Groups that represent the non-religious in Leppa include the Humanistisch Verbond. Christianity comprised 20% of the population. Muslims comprised 10% and other religions (Judaism, Buddhism and Hinduism) comprised the remaining 10%. A 2022 survey from another source found that Protestants outnumbered Catholics.
Transport
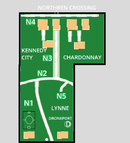
Leppa has 4 main roads, with major motorways N1 and N2 and running through it. All located in Kennedien, With 1 km of public roads, the Leppa has one of the most dense road networks in the world –
See also
Notes
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (April 2023) |
References
- ↑ "Klimaattabel Valkenburg, langjarige gemiddelden, tijdvak 1981–2010" (PDF) (in Nederlands). Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 10 September 2013. Unknown parameter
|url-status=ignored (help) - ↑ "Klimaattabel Valkenburg, langjarige extremen, tijdvak 1971–2000" (PDF) (in Nederlands). Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute. Retrieved 10 September 2013.[permanent dead link]