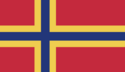
Kingdom of Fatrea
Kingdom of Fatrea | |
|---|---|
|
Flag | |
| Status | Active |
| Official languages | English |
| Religion (2024) | 100% Christian |
| Demonym(s) | Fatrean |
| Government | Unitary Parliamentary Constitutional Monarchy |
• Monarch | Luke I |
| Vacant | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| House of Peers | |
| House of Commons | |
| Independence from the United Kingdom | |
• Founded | 15 February 2024 |
| 15 February 2024 | |
| Population | |
• 2024 estimate | 1 |
| Time zone | UTC+0 (GMT) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+1 (BST) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy |
| Driving side | left |
The Kingdom of Fatrea, more commonly known as Fatrea, is a self-declared sovereign state more commonly known as a micronation by external observers. Founded on 15 February 2024, it is located in Europe. Fatrea is a unitary state under a parliamentary and constitutional monarchy with the king or queen of Fatrea reigning as head of state and a prime minister-led government as the executive governing body. English is the official language of the state.
History
Fatrea was established on 15 February 2024 by King Luke I, with immediate focus being placed on a constitution - which was written and ratified the same day. Since then the nation has been taking an evolutionary stance to its development - establishing what it needs over time and as needed as seen with the armed forces being established on 16 February 2024, and the national bank on 20 February.
Politics and Government
Fatrea is a constitutional and parliamentary monarchy. The monarch serves as head of state and prime minister as head of government. The government is appointed by the monarch and sits in parliament. Executive power is vested in the monarch and cabinet, legislative power in parliament, and judicial power in the Supreme Court and lower courts established by parliament.
Constitution
The constitution provides the basis of the Fatrean political system. It takes some inspiration from the French Charter of 1814. The constitution outlines the powers and duties of the monarchy, the functions of parliament, and the rights and duties of citizens. It also establishes the supreme court and outlines the judicial system more generally, as well as the appointment of ministers. The constitution also suggests some implicit powers the government holds as the central executive body.
Monarchy
The monarchy is the head of state of Fatrea. While the monarchy is constitutional and primarily ceremonial, the constitution vests the monarchy with significant power. The monarch is chief executive, is able to propose bills to parliament, can grant royal assent to or veto bills passed by parliament, is commander-in-chief of the armed forces, appoints and dismisses the government and members of the House of Peers, as well as other powers and duties.
The monarch is advised on how to exercise a number of their powers by the privy council and the government - primarily the prime minister. The privy council consists of members appointed solely at the monarch's discretion as well as cabinet ministers.
The monarchy is hereditary, as prescribed by the constitution.
The current monarch is King Luke I, who took the throne upon establishing Fatrea on 15 February 2024.
Prime Minister
The prime minister of Fatrea is the head of government. They are appointed by the monarch from parliament, and they serve at the monarch's pleasure. The prime minister can originate from either house of parliament, but is typically selected from the House of Commons as it allows the officeholder to be held more accountable by the public. It is the highest office citizens of Fatrea can achieve.
The prime minister chairs the cabinet, nominate ministers, and advises the monarch on the exercise of many of their powers. While not the chief executive, the prime minister leads the executive branch of government. The prime minister is also responsible for ensuring his or her cabinet acts in accordance with the ministerial code.
The prime minister is aided by a deputy prime minister and first secretary of state.
The prime ministry, while having some constitutional roots, was not explicitly established in or by the constitution.
At present, the prime ministry is vacant.
Parliament
Parliament is the supreme legislative body of Fatrea. It is bicameral. The House of Peers sits as the appointed upper house, and the House of Commons sits as the elected lower house. No bill may pass without both the assent of parliament and the monarch. Both houses of parliament are almost perfectly bicameral, with the exception of the proposition of money bills - which may only originate in the House of Commons.
Parliament is called and dissolved by the monarch and sits for annual legislative sessions and terms of up to five years, unless elections are called sooner by the monarch. The prime minister can advise the monarch as to when a general election should be called in accordance with the constitution. Elections are regulated by the electoral commission - an agency that oversees and regulates elections and verifies election results.
Both houses of parliament have a speaker as their presiding officer, appointed by the monarch on the house's nomination, to manage house business and maintain order during debates. The government also appoints an officer to each house to manage government business in each house.
As Fatrea is a parliamentary democracy, the government is appointed from parliament. The prime minister and other government ministers may originate from either house of parliament - as permitted by the constitution. The government is legally responsible to the monarch and politically responsible to parliament.
Judiciary
The judicial system of Fatrea is regulated by the monarch and law. The law establishes courts inferior to the Supreme Court and the monarch appoints all Fatrean judges, who serve at the monarch's pleasure.
The Supreme Court is the highest Fatrean court and specialises in constitutional cases. The Supreme Court is presided over by the Chief Justice of Fatrea. They are responsible for ensuring the executive and legislative branches of government obey the constitution. The Supreme Court is also the highest court of appeals.
Military
The armed forces of Fatrea are the military forces of the state. The armed forces is split into three branches - the Fatrean Army, the Royal Fatrean Navy, and the Royal Fatrean Air Force. The monarch serves as commander-in-chief of the armed forces, and the Chief of the Defence Staff serves as the professional head of the military.
The defence council forms the primary body to oversee the management of the armed forces. All branch chiefs of staff, in addition to the monarch and the secretary of state for defence, sit on the defence council.
The prime minister and secretary of state for defence both have some level of command over the armed forces. As the prime minister directs the government, works with the chancellor of the exchequer to determine the government budget, and advises the monarch on the exercise of many of their powers, the officeholder can exert significant influence over the military.
There is no mandatory military service in Fatrea, but military service is actively encouraged.
Culture
The culture of Fatrea is generally influenced by British culture, particularly Welsh and English culture. Martial arts, particularly Karate, and video games are popular recreational activities amongst citizens. English is the official language of the state. While there is currently no official state religion, Christianity is influential within Fatrea.
National Symbols
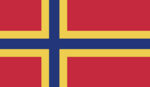
The Fatrean flag is the most distinctive symbol of the state. It was adopted on 24 February 2024 and took inspiration from the nordic flags - most notable the Norwegian flag.
The monarch also sits as a symbol of national culture, and is supported in this role by the great officers of state - nine ceremonial offices appointed by the monarch. Each great officer of state executes different ceremonial duties in support of the state.
Holidays
National holidays are regulated by law and are instated in accordance with key events in national history, celebrating their occurrence. These holidays are held alongside religious holidays which are more freely recognised by the state.
| Date | Name | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| 15 February | Founder's Day | Celebrating the Establishment of Fatrea |
| 16 February | Armed Forces Day | Celebrating the Establishment of Armed Forces |
Economy
While having no official currency, Fatrea does have its own state bank. The bank, alongside the treasury, works to regulate currency affairs in Fatrea as well as to establish and help maintain the economy. The chancellor of the exchequer is the government minister responsible for economic policy.
Geography
Fatrea currently claims the uninhabited island Skorpa which is situated adjacent to Norway. The nation has held this claim since 21 February 2024. As the island is uninhabited and not built on, the nation hopes it can utilise the island for national purposes.