State of Sinorea
This article refers to a micronation or element of micronationalism which is defunct and no longer exists. You can help make the article reflect that or ask on the talk page for further information. |
| Motto: 「受益開明道」 "Benefit the Enlightened Path" | |
| Anthem: 《純度甌》 Chun Du'ou ("Cup of Purity") | |
 | |
| Capital | Nan Lian |
| Largest city | Sai Kung |
| Official languages | Mandarin |
| Recognised regional languages | Cantonese Korean English |
| Official scripts | Hanzi Hangul Latin |
| Ethnic groups | 74.1% Chinese 13.4% Koreans 9.2% British |
| Demonym(s) | Sinorean |
| Government | Federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
• King | Yonghui |
| N/A | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| House of Peers | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Formation | |
• Kingdom | 18 October 2013 |
| 1 April 2016 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 623 km2 (241 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 411.5 |
| Population | |
• 2015 estimate | 56 |
| HDI (2015) | ▲ 0.298 low |
| Currency | Guominbi (¥) / En 元 (SRY) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (CST) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+8 (not observed) |
| Date format | yyyy-mm-dd yyyy年m月d日 (CE; CE+2697) or 國yy年m月d日 |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +886 |
| Internet TLD | .sr .香國 |
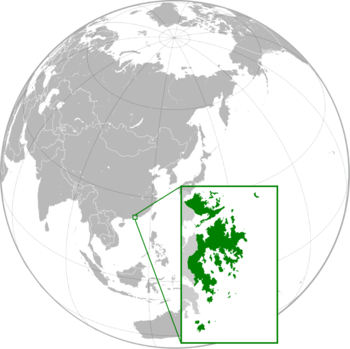
Sinorea (hanzi: 香国; hangul: 향국; pinyin: Xiāngguó; jyutping: Heunggwok; RR: Hyangguk) officially the Commonwealth of Sinorea (hanzi: 香华联邦; hangul: 향화연방; pinyin: Xiānghuá Liánbāng; jyutping: Heungwa Luenbong; RR: Hyanghwa Yeonbang), is a self-declared sovereign state constituting the Eastern New Territories, Hong Kong. Located on the southern coast of China at the Pearl River Estuary and the South China Sea, neighbouring states include Hong Kong to the east, China to the north, and Taiwan to the east. The Hanzi that make up Sinorea's name mean "Fragrant Kingdom", and Sinorea is often called the "Land of the Fragrant Spirit".
Sinorea consists a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy. About 10% of Sinorea's claim is mostly claimed but uncontrolled. Nan Lian is the capital city and seat of government located in the Sinorean Capital territory. Sinorea has claimed complete independence since 18 October 2013, the day when the country was declared.
Sinorea consists of three states and one mainland territory: Sai Kung, Nam Kwan, Bak Kui and the Sinorean Capital Territory. The regions are subdivided into federal states, each represented by a council which advises the government on local matters such as public facilities, community programmes, cultural activities, and environmental improvements.
Sinorea's history goes back since the Treaty of Nanking. King Yonghui has declared the Commonwealth of Sinorea to be the successor to British Hong Kong that ceased to exist in 1997. Today, most of Sinorea's political influence is based on the former British colony.
Etymology
The English word Sinorea derives from China in Latin and Korea in English (Sino and rea); the country's cultural influences came from China and Korea. However, the first dynasty of Sinorea were the House of Yi; former Korean monarchs who were proclaimed allegiance as the royal family of Sinorea by the government from 2013 to 2016, although Queen Haewon did not recognize her reign in Sinorea.
The official name of the modern country is the Commonwealth of Sinorea (hanzi: 香华联邦; hangul: 향화연방; pinyin: Xiānghuá Liánbāng; jyutping: Heungwa Luenbong; RR: Hyanghwa Yeonbang). The common Mandarin names for the country are Xiāngguó (Hanzi: 香国, from Xiāng, fragrant, and guó, "state" or "states", and in modern times, "nation") and Xiānghuá (Hanzi: 香华), although the country's official name has been changed numerous times by successive dynasties and modern governments. The term 'Xiāngguó appeared in various ancient texts, such as the Classic of History. The term, which can be either singular or plural, referred to the group of states or provinces in the central land, but was not used as a name for the country as a whole until the nineteenth century. The Sinoreans were not unique in regarding their country as "central", with other civilizations having the same view of themselves.
History
British Hong Kong

Hong Kong was given by the Qing Dynasty to the British Empire in 1841 under the Treaty of Nanking. Kowloon was added to the area of Hong Kong in 1860 under the Convention of Peking, and New Territories was added in 1898 under the Second Convention of Peking. In 1941–1945, Hong Kong was ruled by the Japanese Empire during World War II. In 1984, People's Republic of China and the United Kingdom agreed under Sino-British Joint Declaration on the Question of Hong Kong that Hong Kong was to be returned to China on 1 July 1997.
Kingdom of Sinorea
Due to the Hong Kong independence movement, instead of supporting the either the colonists or the independence supporters, the Sinorean Provisional Government decided to declare Eastern Hong Kong New Territories independency under a new state entity. Around May 2013, the Provisional Government instructed its followers to canvass support for the creation of the Kingdom of Sinorea. The Sinorean Provisional Government moved forward to separate the Eastern New Territories from Hong Kong, thus was not approved by the Hong Kong Government. On 18 October 2013, the the Kingdom of Sinorea was declared and to create an air of legitimacy, the government proclaimed its allegiance to Yi Hae-won, the contender to the Korean throne, to be the Queen of Sinorea. Despite Yi Hae-won was first to accede the throne, Yi Gu was awarded posthumously as the first King of Sinorea. However, Yi Hae-won's reign remained unrecognized by herself.
The Yi-Lee Transition took place in 2016, Queen Haewon was forced to abdicate in favor of the House of Lee due to inactivity and not recognizing her role as Queen. Yonghui succeeded the Sinorean throne on 3 March 2016, and during his reign the Kingdom of Sinorea became the Commonwealth of Sinorea, adopting political influences from Australia and the former British colony.
External links
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2023) |

